6. Object attributes
Attributes (formerly called “metakeys”) are used to store associations with external systems and other extra information about an object.
List of object attributes can be found in detailed object view in the Attributes box.
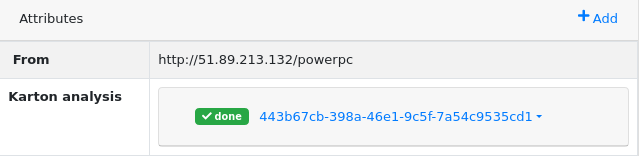
How attributes can be used?
Attributes are set of unique key-value pairs, ordered from the earliest added. Keys are not arbitrary and must be defined first in attribute configuration. Each attribute key can have special properties depending on the key semantics.
Attribute feature was initially designed to store the analysis identifier. Attribute values can be rendered as URLs to the external webpage with analysis details.
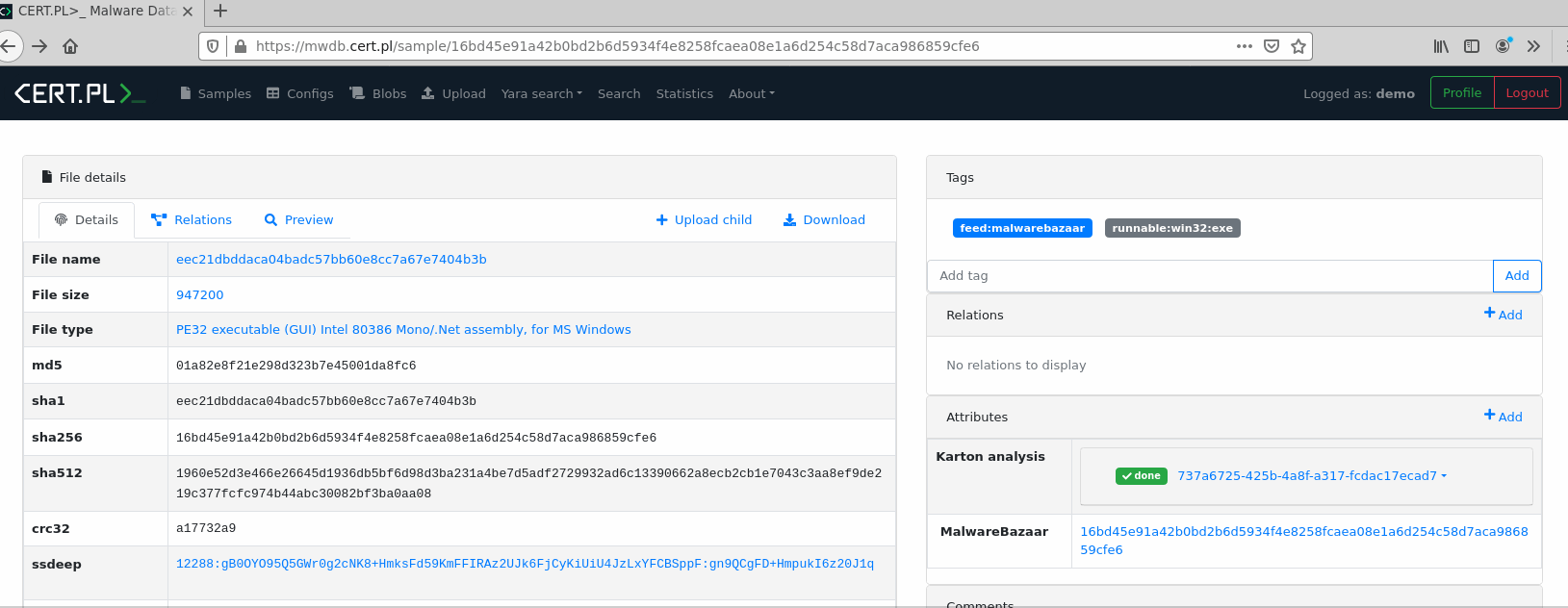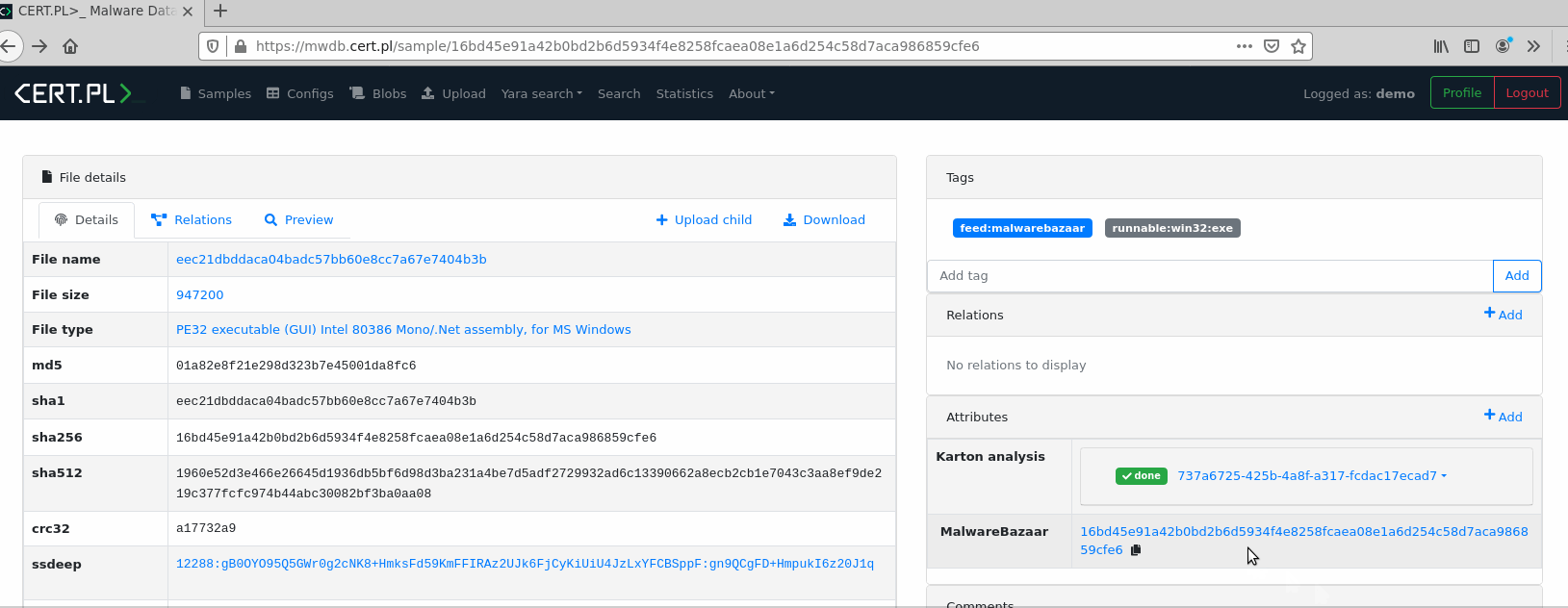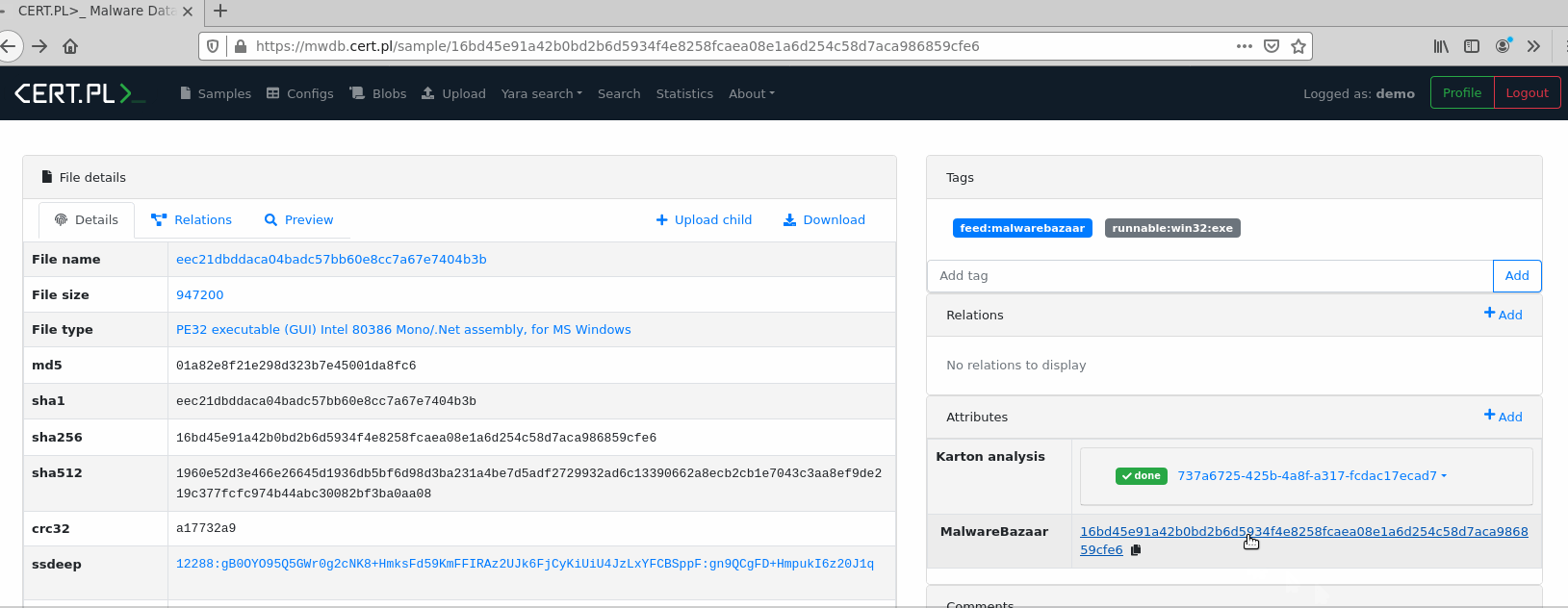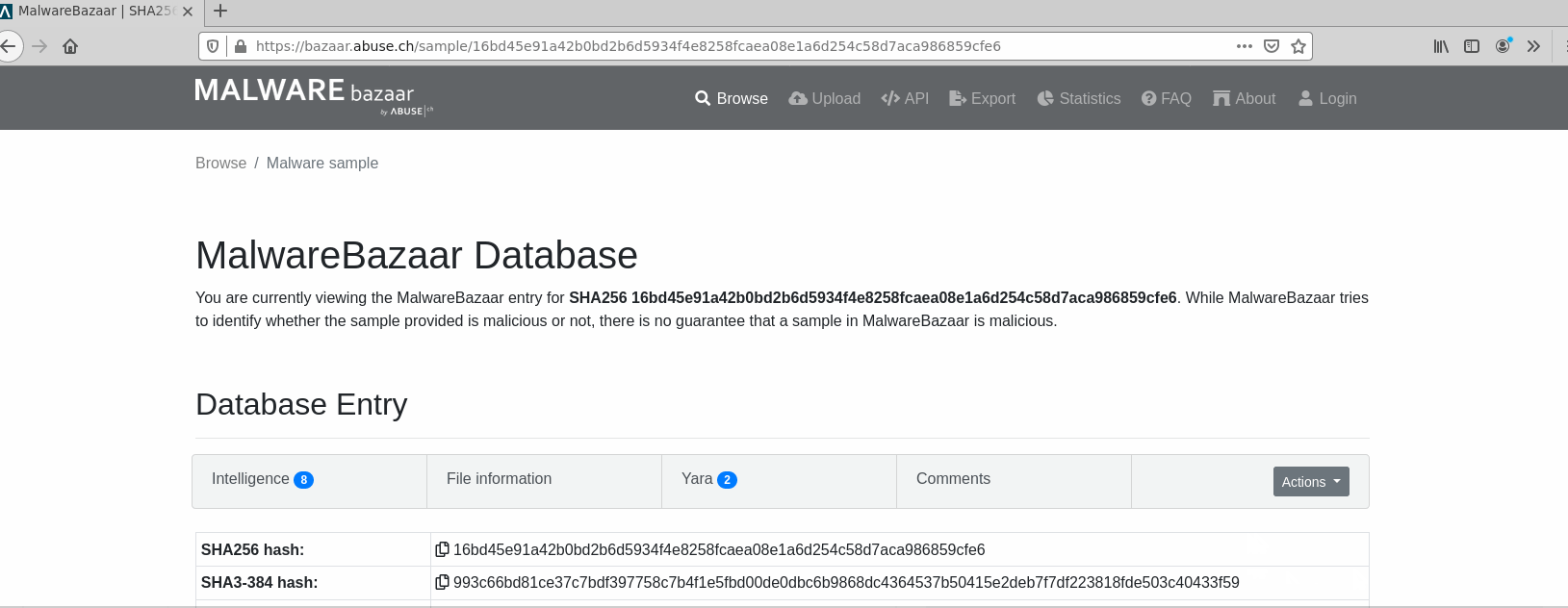
Plugins can apply custom rendering of attribute values to include additional information from external systems. Good example is Karton plugin that uses custom component to show information about analysis status.
Declaring new attribute
Attributes must be declared first by administrator (having manage_users capability). To declare a new attribute, go to the Settings → Attributes view using navigation bar.
Then, click on Create attribute button.
Attribute key has few basic properties described below:
Key - the main attribute key name. Identifies the key and is used in API. Must contain only lowercase letters and digits and maximum 32 characters are allowed.
Label (optional) - user-friendly label for attribute, visible for MWDB users instead of key. Can be changed any time you want.
Description (optional) - description to explain users the semantics of attribute, visible in MWDB UI.
URL template (optional) - URL template used to map the values to the URLs. Template can contain
$valueplaceholder, where MWDB UI will put the attribute value and make clickable link.Hidden attribute (optional) - Actually it should be called “protected attribute”. These attributes have special purpose and are described further.
After defining new attribute, click Submit. The most important thing at this step is to choose good attribute key. Don’t worry much about the optional fields, they can be changed any time you want.
When attribute is added, you will be redirected to the attribute key settings page. It looks almost the same, but have additional box at the bottom with ACL (access control list) settings for groups.
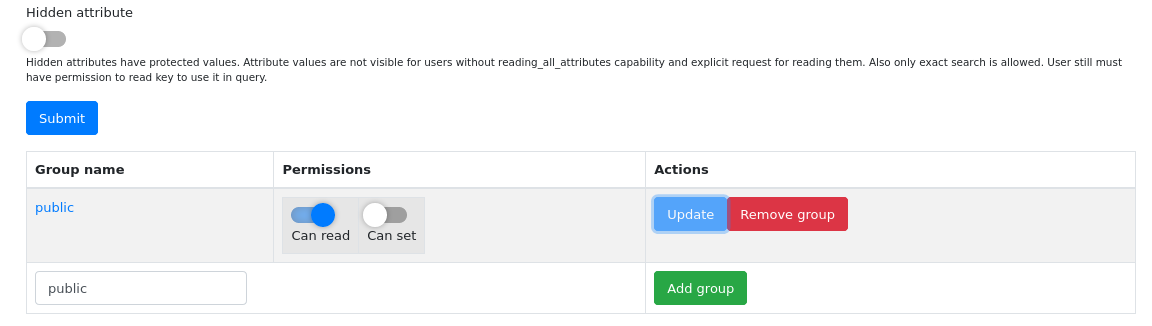
Attributes without ACLs are accessible only for administrators or users with special capabilities like Has access to all attributes of object and Can add all attributes to object. Regular users can’t see and set the attributes without explicit permission.
If you want to give permission to the specific group or user, type the group name (or user login) and click Add group. Then you can use Can read and Can set switches to set the permissions. Apply changes for group using Update button.
If attribute should be available to all users in MWDB instance, add public group with Can read permission. If you want all users to add new values with defined attribute key - additionally enable Can set permission.
Adding attributes to objects
If you have permission to set the attribute key, you can add a new attribute value using Add + button placed in Attributes box header.
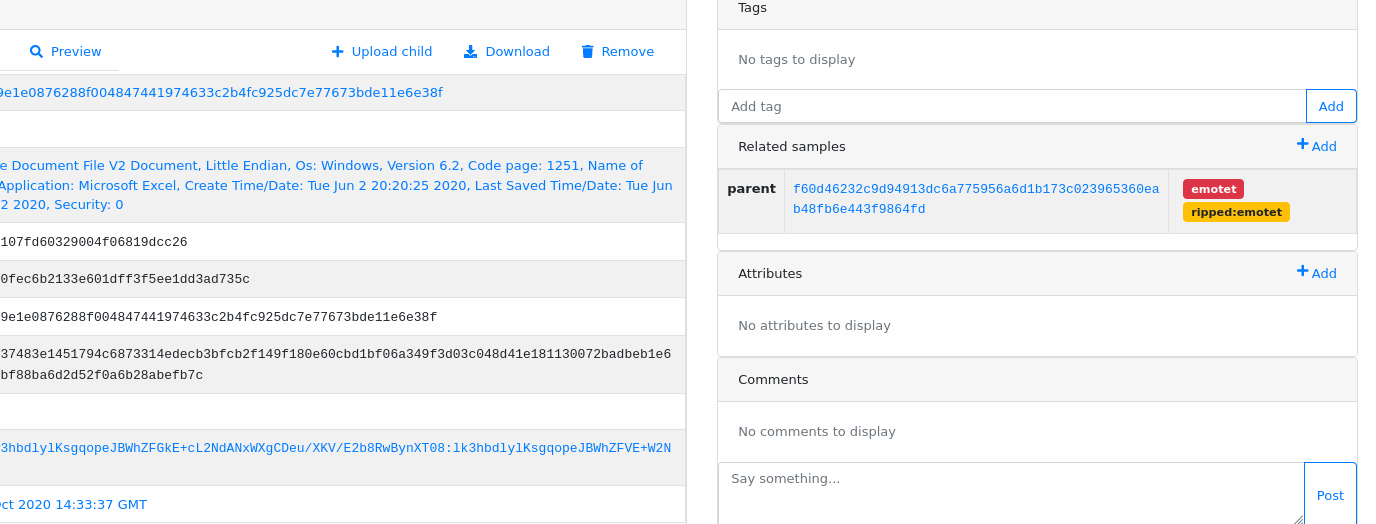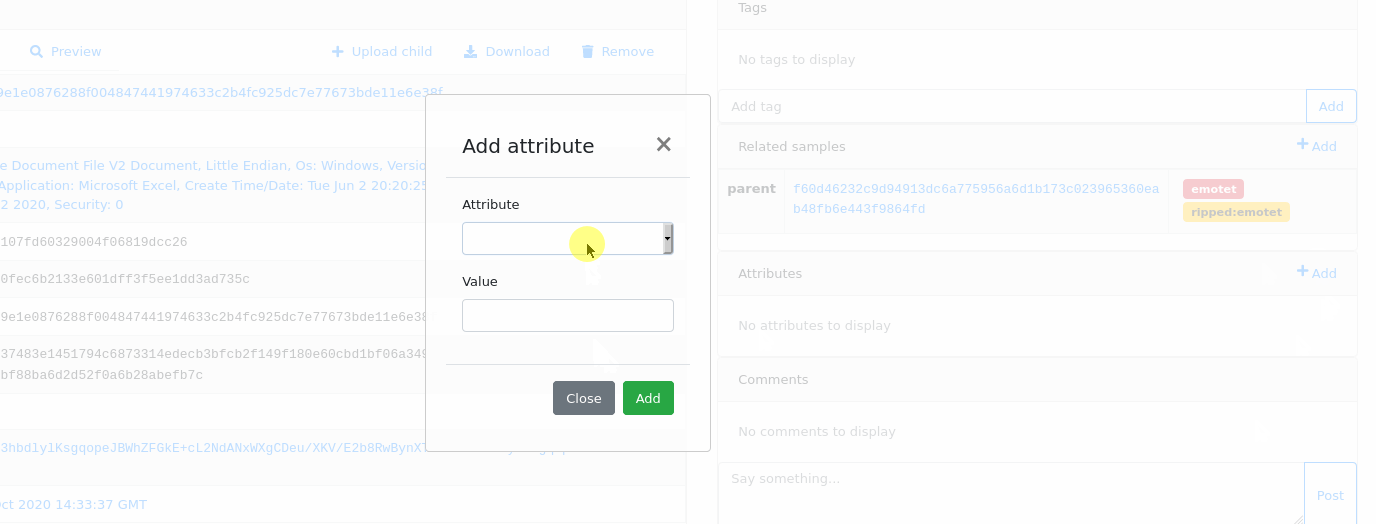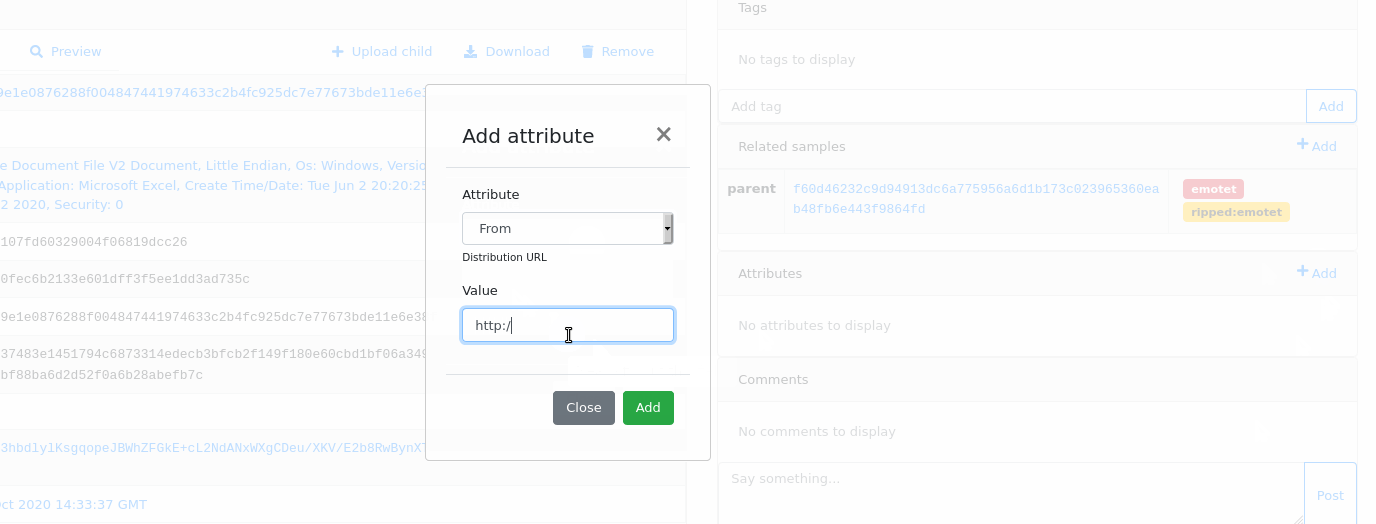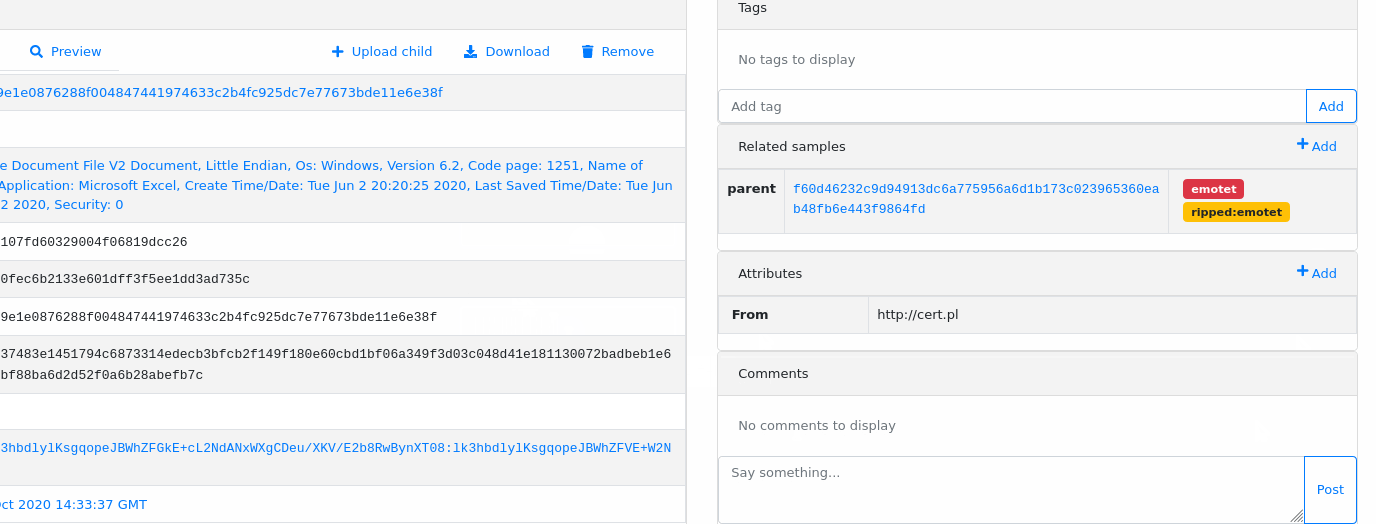
Attributes can be added during object upload. It’s really useful if you want to use attributes as plugin arguments e.g. to provide password to the encrypted file/archive. Attributes passed that way will be set just before the plugin hook fires.
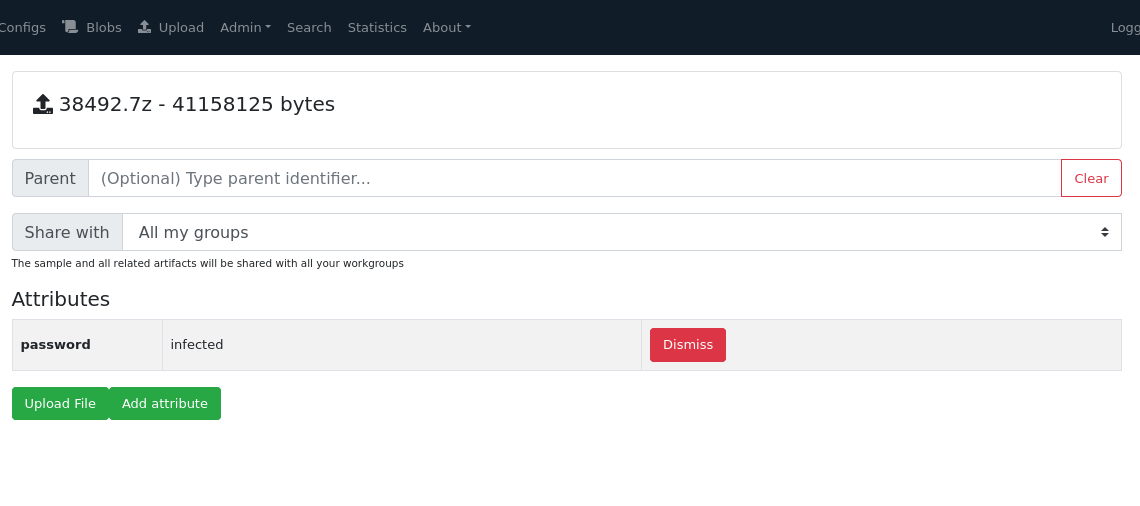
Another use case is passing source feed identifier with the uploaded file.
The same operations can be performed using mwdblib. Let’s explore the attributes in mwdb.cert.pl:
from mwdblib import MWDB
mwdb = MWDB(api_key=..., api_url=...)
file_object = mwdb.query_file("d9f00cc51e1c107881ebeaa0fd4f022a")
print(file_object.attributes)
# {'from': ['http://45.95.168.97/bins/sora.x86'],
# 'karton': ['da83d95a-0564-4d32-8fea-ff61ac7396d1']}
To add a new attribute to the existing object, use MWDBObject.add_attribute function. Example below will fail in mwdb.cert.pl because attribute test-key is probably undefined, but you can try it on your own instance!
file_object.add_attribute("test-key", "test-value")
print(file_object.attributes)
# {'from': ['http://45.95.168.97/bins/sora.x86'],
# 'karton': ['da83d95a-0564-4d32-8fea-ff61ac7396d1'],
# 'test-key': ['test-value']}
To pass an attribute value during upload, you can set it via attributes argument using MWDB.upload_file routine.
mwdb.upload_file("infected.zip",
zip_contents,
attributes={
"test-key": "test-value"
})
JSON-like attribute values
Starting from 2.6.0, MWDB Core attribute values are not limited to be plain strings, but also JSON-like objects.
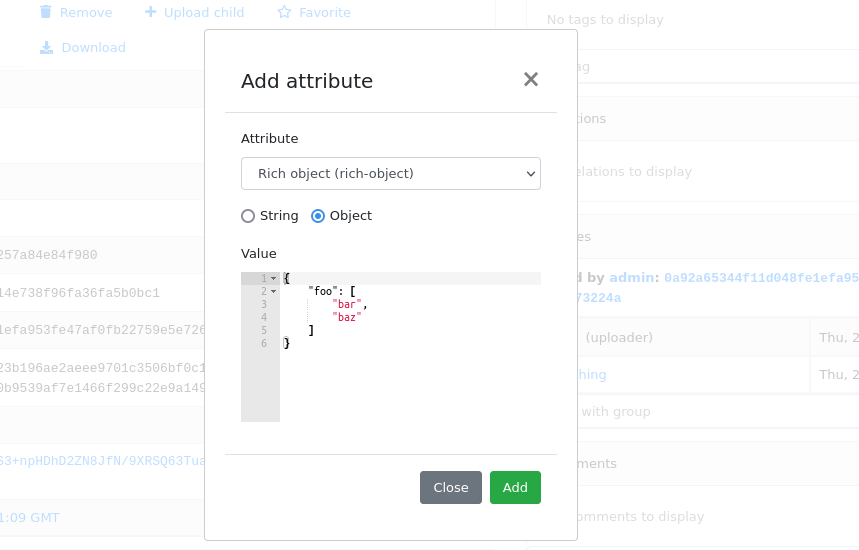
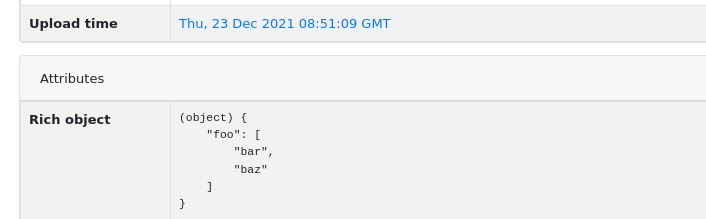
Using JSON attributes, you can easily store complex data like:
enrichments from other services
file static analysis information like code signing, sections, list of resources
information about produced dumps from sandbox
file_object.add_attribute(
"dumps", {
"fffb0000_1908f226280751a1": {
"apivector": "A45oA36CA7BA15iAgA6gA3CABQAEA3IAAQQA5CAGBkACA4QA6JIAAICISIMhY]Us",
"families": [
"isfb"
],
"similarity": 0.35330578512396693
},
"fffa0000_568d29558bebb4d8": {
"apivector": "A119CABQAEACA4QAAgA4BEA21QwMEhYQUM",
"families": [
"isfb"
],
"similarity": 0.3490675028882654
}
}
)
You can also search for parts of object value using JSON queries, like for configuration contents:
attribute.dumps.fffb0000_1908f226280751a1.families*:isfb
Removing attributes from objects
To remove attribute value, hover over that value and click the remove button.
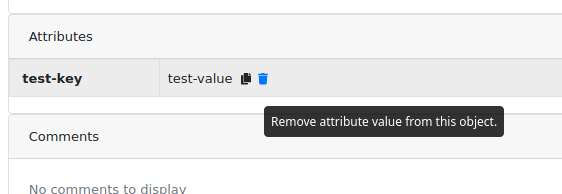
Attribute can be removed only if user has permission to set the attribute key and has removing_attributes capability turned on.
Rich templates
Starting from v2.8.0, MWDB Core supports rich attribute value rendering. For more information, see Rich attributes guide.