Integration guide
MWDB comes with advanced plugin engine, which allows to add new API features, integrate MWDB with other systems using webhooks and extend MWDB UI functionality.
Plugins are used by mwdb.cert.pl to:
integrate MWDB with malware analysis backend and reporting systems
provide new features like mquery search
customize mwdb.cert.pl instance
Note
This chapter describes only the most basic features of plugin system, allowing to write simple integrations. More plugin system features will be documented in the near future.
Getting started with local plugins
Backend plugins are just Python packages imported by MWDB from specified location. Let’s check the plugin settings in mwdb.ini:
### Plugin settings
# Set enable_plugins to 0 to turn off plugins (default: 1)
# enable_plugins = 0
# List of plugin module names to be loaded, separated by commas
# plugins =
# Directory that will be added to sys.path for plugin imports
# Allows to load local plugins without installing them in site-packages
# local_plugins_folder = ./plugins
# Autodiscover plugins contained in local_plugins_folder (default: 0)
# local_plugins_autodiscover = 1
Plugins can be loaded from installed packages or imported from local_plugins_folder.
Let’s create a simple, local hello_world plugin:
plugins
└── hello_world
└── __init__.py
and put short description in __init__.py file:
__author__ = "just me"
__version__ = "1.0.0"
__doc__ = "Simple hello world plugin"
Then, set mwdb.ini file to load your hello_world plugin. If you configured mwdb-core to use current directory, you should find that file there. If not, you can still overwrite the mwdb.ini settings by creating another mwdb.ini file in the current working directory, where mwdb-core run is invoked.
[mwdb]
...
plugins = hello_world
local_plugins_folder = ./plugins
Let’s run the mwdb-core:
$ mwdb-core run
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: off
[INFO] MainThread - plugins.load_plugins:141 - Loaded plugin 'hello_world'
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
As you can see in logs, your plugin has been loaded successfully. You can additionally check that using /about endpoint in UI.
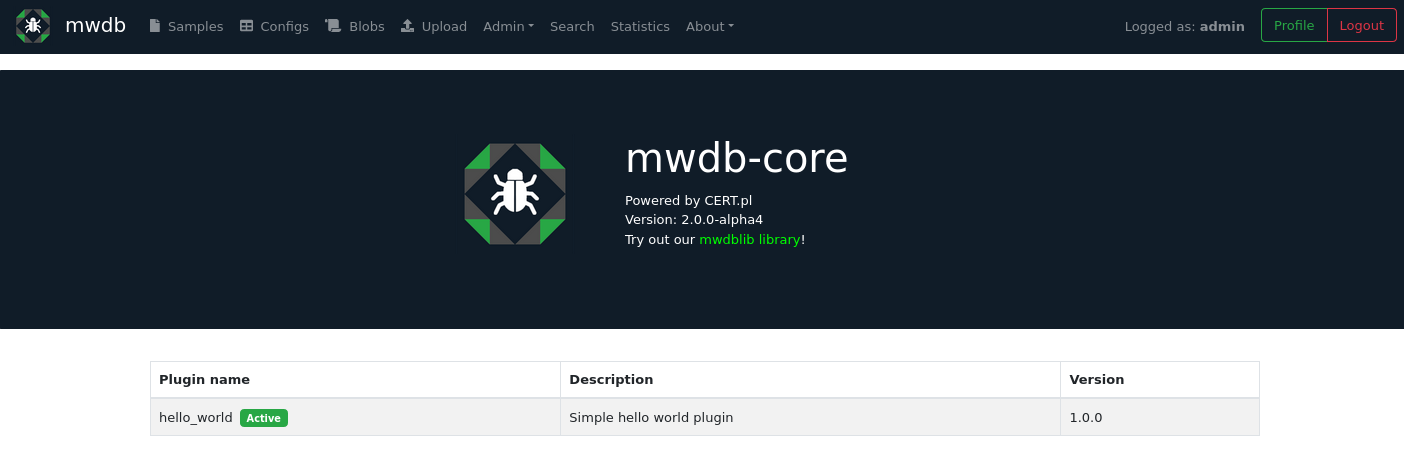
Adding webhook
Now, let’s make it a bit more useful and add the actual webhook. When plugin module is loaded by MWDB, it calls the entrypoint function named __plugin_entrypoint__.
Modify the __init__.py file to implement simple entrypoint saying “Hello world!”.
import logging
from mwdb.core.plugins import PluginAppContext
__author__ = "just me"
__version__ = "1.0.0"
__doc__ = "Simple hello world plugin"
logger = logging.getLogger("mwdb.plugin.hello_world")
def entrypoint(app_context: PluginAppContext):
logger.info("Hello world!")
__plugin_entrypoint__ = entrypoint
The expected result is:
$ mwdb-core run
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: off
[INFO] MainThread - __init__.entrypoint:14 - Hello world!
[INFO] MainThread - plugins.load_plugins:141 - Loaded plugin 'hello_world'
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
PluginAppContext object allows to provide extension for MWDB like adding webhook handler and extending the API.
Webhook handler is implemented by providing a new class that inherits from PluginHookHandler. New handler class can be then registered using app_context.register_hook_handler method.
import logging
from mwdb.core.plugins import PluginAppContext, PluginHookHandler
from mwdb.model import File
__author__ = "just me"
__version__ = "1.0.0"
__doc__ = "Simple hello world plugin"
logger = logging.getLogger("mwdb.plugin.hello_world")
class HelloHookHandler(PluginHookHandler):
def on_created_file(self, file: File):
logger.info("Nice to meet you %s", file.file_name)
def on_reuploaded_file(self, file: File):
logger.info("Hello again %s", file.file_name)
def entrypoint(app_context: PluginAppContext):
logger.info("Hello world!")
app_context.register_hook_handler(HelloHookHandler)
__plugin_entrypoint__ = entrypoint
After applying above modifications to __init__.py, let’s restart mwdb-core and add a new to file and check if it works.
[INFO] Thread-3 - __init__.on_created_file:16 - Nice to meet you evil.exe
[INFO] Thread-3 - object.create_object:88 - File added - dhash:9e302844386835ef50bec3017e2c60705ab6bf33e4849e58e3af19a605b46d00 - is_new:True
...
[INFO] Thread-12 - __init__.on_reuploaded_file:19 - Hello again evil.exe
[INFO] Thread-12 - object.create_object:88 - File added - dhash:9e302844386835ef50bec3017e2c60705ab6bf33e4849e58e3af19a605b46d00 - is_new:False
Webhooks can be used to automatically analyze the uploaded file in sandbox. The good example is mwdb-plugin-drakvuf which implements webhook that sends all uploaded files to the Drakvuf Sandbox for analysis.
Check out mwdb-plugin-drakvuf on Github!
Available hooks
A lot of hooks have been implemented in MWDB. Each of these hooks is triggered when particular event occurs in system.
List of available hooks and events triggering these hooks.
on_created_object(self, object: Object)- object was uploaded (file, blob or config) or pulled from remoted resourceon_reuploaded_object(self, object: Object)- object was again uploaded or pulled from remote resourceon_removed_object(self, object: Object)- object was deletedon_created_file(self, file: File)- file was uploaded or pulled from remoted resourceon_reuploaded_file(self, file: File):- file was again uploaded or pulled from remote resourceon_removed_file(self, file: File)- file was deletedon_created_config(self, config: Config)- config was uploaded or pulled from remoted resourceon_reuploaded_config(self, config: Config)- config was again uploaded or pulled from remote resourceon_removed_config(self, config: Config)- config was deletedon_created_text_blob(self, blob: TextBlob)- text blob was uploaded or pulled from remoted resourceon_reuploaded_text_blob(self, blob: TextBlob)- text blob was again uploaded or pulled from remote resourceon_removed_text_blob(self, blob: TextBlob)- text blob was deletedon_created_tag(self, object: Object, tag: Tag)- a new tag was created and assigned to objecton_reuploaded_tag(self, object: Object, tag: Tag)- tag was again assigned to objecton_removed_tag(self, object: Object, tag: Tag)- tag was removed from objecton_created_comment(self, object: Object, comment: Comment)- a new comment was created and assigned to objecton_removed_comment(self, object: Object, comment: Comment)- comment was removed from objecton_created_relation(self, parent: Object, child: Object)- relation between parent and child objects was addedon_removed_relation(self, parent: Object, child: Object)- relation between parent and child objects was removedon_created_attribute_key(self, attribute_def: AttributeDefinition)- attribute definition was createdon_updated_attribute_key(self, attribute_def: AttributeDefinition)- attribute definition was updatedon_removed_attribute_key(self, attribute_def: AttributeDefinition)- attribute definition was removedon_created_attribute(self, object: Object, attribute: Attribute)- attribute was assigned to objecton_removed_attribute(self, object: Object, attribute: Attribute)- attribute was removed from objecton_created_user(self, user: User)- a new user account was created (also using OpenID Provider)on_removed_user(self, user: User)- user account was removedon_updated_user(self, user: User)- user account was updatedon_created_group(self, group: Group)- a new group was created. Also when a new user is registered and his private group is createdon_removed_group(self, group: Group)- group was removed. Also when a user is deleted and his private group is removedon_updated_group(self, group: Group)- group attributes where updatedon_created_membership(self, group: Group, user: User)- user was added to the groupon_removed_membership(self, group: Group, user: User)- user was removed from the groupon_updated_membership(self, group: Group, user: User)- membership was updatedon_changed_object(self, object: Object)- this hook is triggered when one of the undermentioned events takes place:a new tag was created and assigned to object
tag was removed from object
a new comment was created and assigned to object
comment was removed from object
relation between parent and child objects was added
relation between parent and child objects was removed
attribute was assigned to object
attribute was removed from object
Creating web plugins
MWDB Core comes with powerful web plugin engine which allows to extend almost any component within MWDB UI. For a long time it was an undocumented feature used mainly by mwdb.cert.pl service and built on top of Create React App hacks and overrides.
Starting from v2.9.0 release, we’re using joined powers of Vite and Rollup to make it a real thing.
Web plugins: getting started
Frontend plugins are a very different animal from Python backend plugins and you may need a bit more knowledge about build-time mechanisms.
Let’s go to the docker/plugins directory within mwdb-core repository and extend our hello_world plugin:
docker
└── plugins
└── hello_world
└── __init__.py
+ └── index.jsx
+ └── package.json
First is package.json that contains short specification of our plugin. Name must contain @mwdb-web/plugin- prefix.
{
"name": "@mwdb-web/plugin-hello-world",
"version": "0.0.1",
"main": "./index.jsx"
}
Finally we can write simple plugin that adds new Hello world page. Let’s check ``index.jsx` contents:
// Imports from React and Font Awesome libraries
import React from 'react';
import { Route, Link } from 'react-router-dom';
import { FontAwesomeIcon } from "@fortawesome/react-fontawesome";
import { faHandHoldingHeart } from "@fortawesome/free-solid-svg-icons";
// Import from MWDB Core commons and components
import { View } from "@mwdb-web/commons/ui";
import { AboutView } from "@mwdb-web/components/Views/AboutView";
function HelloWorld() {
return (
<View>
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
Nice to see you!
<hr />
<About/>
</View>
)
}
export default () => ({
routes: [
<Route path='hello' element={<HelloWorld />} />
],
navbarAfter: [
() => (
<li className="nav-item">
<Link className="nav-link" to={"/hello"}>
<FontAwesomeIcon
className="navbar-icon"
icon={faHandHoldingHeart}
/>
Hello there!
</Link>
</li>
)
],
})
After setting up all of the things, run docker-compose -f docker-compose-dev.yml build and docker-compose -f docker-compose-dev.yml up
to run the application. If everything is OK, you should see the results like below:
<show the result>
But what actually happened in that index.jsx file? there are lots of things going there!
Let’s focus on most important ones:
Line starting with
export defaultis actually an entrypoint of our plugin. It exports callback that is called after plugin is loaded.Entrypoint callback is expected to return an object that contains specification of extensions provided by plugin.
Our plugin contains two extensions: *
routesthat implement React Router routes to be included in web application *navbarAfterbeing a list of React component functions that will be rendered afternavbarPlugins adds new navbar button
Hello there!and/helloroute renderingHelloWorldcomponent. Our new component usesViewfrom@mwdb-web/commons/uiwhich is common wrapper for main views used within application. In addition, it rendersAboutview imported from@mwdb-web/componentsjust under our gretting.
But where is actual list of possible extensions defined? They’re defined in core application code and can be found
by references to few methods and wrappers from common/plugins :
fromPluginscollects specific type of extension from all loaded plugins and returns a list of them. For example: newroutesto be added.Extensiondoes the same but treats all collected objects as components and renders them.Extendablewraps object with<name>Before,<name>Replaceand<name>Afterextensions, so we can add extra things within main views.
So navbar is one of Extendable wrappers that can be found within application and that’s why we can add extra navbar item.
Web plugins: how it works internally?
There are two requirements to be fulfilled by the plugin engine:
Plugin code needs to be loaded and executed along with the core application
Plugin must be allowed to reuse and extend the core application parts
MWDB uses Rollup import aliases and Vite virtual modules to make a link between plugin code and the core.
Vite build runtime looks for
@mwdb-web/plugin-*packages that are installed innode_modulesThey can be regular packages or just links (see also npm-link)
@mwdb-web/pluginsvirtual module defines dynamic imports that are further resolved by Vite to create separate bundles for plugins that can be asynchronically loaded.Virtual module code looks like below:
export default { "plugin-example": import("@mwdb-web/plugin-example"), ... }
@mwdb-web/pluginspackage is then resolved at runtime bycommons/pluginsloader that resolves dynamic imports and collects hook specification. Plugins are loaded before first render occurs.
When plugin loader finishes its job, initial render kicks in and plugin is finally able to extend the application.
MWDB uses Rollup capabilities to make plugins able to use components from web source root (mwdb/web/src) and expose them
as @mwdb-web/* aliases:
@mwdb-web/commonscontains core parts of application that are expected to be used by plugins as well. Main packages are:apimodule serving backend REST API bindings built on top of Axiosauthmodule servingAuthContextwith information about currently authenticated userconfigmodule with current server configuration and useful globalshelperswith useful helper methodsuiwith UI components and utilities
@mwdb-web/componentscontains implementation of all application views and there is higher chance that something will break across the versions if you use them directly.
Building customized images
If you want to extend MWDB with new features using the plugin system, it’s always useful to be able to build your own customized Docker images.
There are two ways to do that:
Simple way: clone https://github.com/CERT-Polska/mwdb-core repository. Then place your plugins in
docker/pluginsand use Dockerfiles fromdeploy/dockerto build everything from scratch.More extensible way: use
certpl/mwdbandcertpl/mwdb-web-sourceas base images and make your own Dockerfiles. This method enables you to install additional dependencies and provide custom plugin-specific overrides.
Building custom backend image is simple as in Dockerfile below:
# It's recommended to pin to specific version
ARG MWDB_VERSION=v2.9.0
FROM certpl/mwdb:$MWDB_VERSION
# Install any Alpine dependencies you need
RUN apk add p7zip
# Install any Python dependencies you need (certpl/mwdb image uses venv internally)
RUN /app/venv/bin/pip install malduck
# Copy arbitrary backend plugins and mail templates
COPY mail_templates /app/mail_templates
COPY plugins /app/plugins
Backend plugins are linked in runtime, so that part is pretty easy to extend. A bit more complicated thing is frontend part:
ARG MWDB_VERSION=v2.9.0
FROM certpl/mwdb-web-source:$MWDB_VERSION AS build
# Copy web plugins code
COPY plugins /app/plugins
# Set workdir to /app, install plugins to ``/app/node_modules`` and rebuild everything
WORKDIR /app
RUN npm install --unsafe-perm $(find /app/plugins -name 'package.json' -exec dirname {} \; | sort -u) \
&& CI=true npm run build
# Then next stage is copied from https://github.com/CERT-Polska/mwdb-core/blob/master/deploy/docker/Dockerfile-web
# You need to copy start-web.sh and ngnix.conf.template as well, or adapt them according to your needs
FROM nginx:stable
LABEL maintainer="admin@example.org"
ENV PROXY_BACKEND_URL http://mwdb.:8080
COPY nginx.conf.template /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf.template
COPY start-web.sh /start-web.sh
COPY --from=build /app/dist /usr/share/nginx/html
# Give +r to everything in /usr/share/nginx/html and +x for directories
RUN chmod u=rX,go= -R /usr/share/nginx/html
# By default everything is owned by root - change owner to nginx
RUN chown nginx:nginx -R /usr/share/nginx/html
CMD ["/bin/sh", "/start-web.sh"]
Room for improvement
Plugin system was created mainly for mwdb.cert.pl, so not everything may fit your needs. Also things may break from time to time, but as we maintain our internal plugins ourselves, most important changes will be noted in changelog. You can also find broader explanation and migration recipes in What’s changed chapter.
So if you need another Extendable place within UI or yet another hook within backend: feel free to create issue on
our GitHub repository.